White-handed Gibbon
White-handed Gibbon
Hylobates lar

White-handed Gibbon
White-handed Gibbon
Hylobates lar

-
Class
Mammalia -
Order
Primates -
Familly
Hylobatidae
-
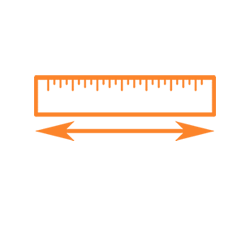 45–63cm
45–63cm -
 5–8kg
5–8kg -
 6 months
6 months -
 1
1 -
 40 years
40 years
-
Diet
omnivorous (mainly fruits, leaves, young shoots, eggs, insects) -
Habitat
tropical forest -
Range
South-east Asia and Malay Archipelago -
 This species is part of a European Breeding Program
This species is part of a European Breeding Program
-
Population in the wild
En diminution -
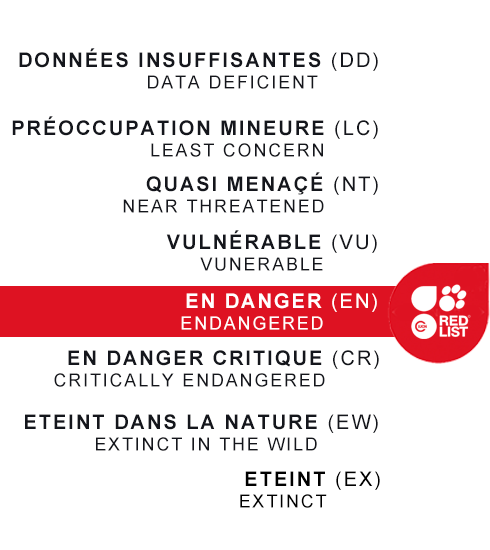
IUCN REDLIST status

White-handed Gibbons can have cream, brown or black fur, whatever their gender or age.
Females produce a single young after a pregnancy lasting about 6 months. Babies start to ingest solid food and leave their mother at about the age of 4 months.
Gibbons are aerial creatures who move in a spectacular way called ‘brachiation’, which allows them to swing quickly from branch to branch and jump at a height of more than 10m.
Males and females usually mate for life. They communicate in a complex way, based on visual postures and very loud sounds. The alternating or simultaneous song produced by males and females mainly serves to demarcate their territory, which covers several tens of hectares. The tone varies by gender.





